RF & Microwave Engineering Blog Posts
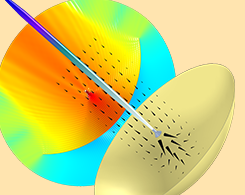
The Internet of Space Takes Off with Advanced Antenna Designs
You’ve heard of the Internet of Things, but what about the Internet of Space, which change how we share information and communicate worldwide. A key aspect of this concept: antenna designs.
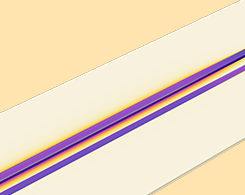
Analyzing Time-Domain Reflectometry for 2 Electrical Designs
Here are 2 examples of analyzing the signal integrity and time domain reflectometry in electrical devices: a high-speed interconnect and a set of parallel microstrip lines.
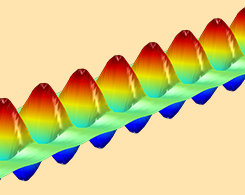
Simulating Extraordinary Optical Transmission at Terahertz Frequencies
One potential approach to improving medical imaging, quality assurance, and other terahertz applications is extraordinary optical transmission, a process that can be studied with RF simulation.
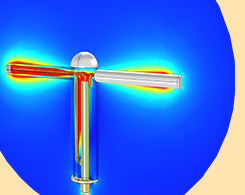
Optimizing the Geometry of Optical Antennas with Genetic Algorithms
What does antenna design have to do with the concept of natural selection? Although it may sound far-fetched, the basic principles of natural selection can be used to optimize antenna geometries.
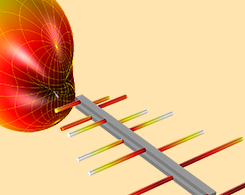
Designing Accurate EMC/EMI Testing Equipment with RF Modeling
EMI/EMC testing is used to ensure that various products, processes, and systems meet standard compliance requirements. RF modeling can be used to design equipment for accurate analyses.
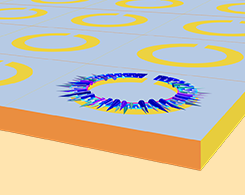
Streamlining the Design of Frequency-Selective Surfaces
If you want to improve the frequency response of a frequency-selective surface, you have many options for methods. 1 method streamlines what can be a complex process: simulation applications.
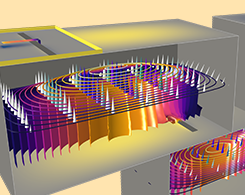
Introduction to Designing Microwave Circuits Using EM Simulation
When it comes to designing RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave circuits with electromagnetics simulation, the key is to start simple and gradually add complexity to your analyses.
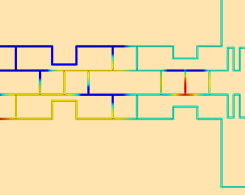
Designing a Butler Matrix Beamforming Network with RF Modeling
Check out a tutorial model with implications in developing the 5G mobile network: Butler matrix beamforming networks, which can be combined with phased array antennas for wireless communication.
