
When using COMSOL Multiphysics on a Floating Network License, it is possible to use the Client-Server mode of operation to access remote computing resources for solving large models, while still using the graphics card on a local machine to display graphics. This can have some significant advantages, so let’s look at Client-Server mode in more detail.
Computers Are Fast, Networks Are (Relatively) Slow
Serious engineering and scientific computing problems involve working with large amounts of data — anywhere from megabytes to gigabytes of data are commonly generated during a COMSOL Multiphysics simulation. To generate and store this data, we will want to use computers with fast processors, a lot of Random Access Memory (RAM), and a large hard drive. To visualize this data, it is important to have a high-end graphics card.
The COMSOL Multiphysics workflow can be divided into four steps:
- Preprocessing: Creating the geometry and defining the physics. The user is constantly interacting with the user interface (UI), but this step is usually not very computationally intensive.
- Meshing: This step can require a lot of interaction with the UI and can also be computationally demanding.
- Solving: This is the most computationally demanding step. However, the user only rarely interacts with the UI.
- Postprocessing: The most interactive step. Most of the computations are handled by the graphics card.
Under ideal conditions, everyone would be working on a high-end computer with more than enough memory and processing power for all of these steps. But realistically, we have to make do with what is available on each user’s desktop. If we need to solve larger models, we will want to access a shared computing resource across a network.
Here lies the issue: Passing data back and forth across a network is a lot slower than passing data around inside your computer, especially when it comes to the graphics-intensive postprocessing step. This becomes particularly apparent when using a virtual desktop application, which has to continuously send many megabytes of graphics data over the network. So, let’s see how the COMSOL Multiphysics Client-Server mode addresses this issue.
One COMSOL Multiphysics Floating Network License is used during Client-Server operation.
Client-Server Mode Maximizes Efficiency
Users typically start COMSOL Multiphysics on their local desktop or laptop computer and start drawing the geometry, defining material properties, applying loads, and setting boundary conditions. Since this primarily involves selecting objects on the screen and typing, the computational requirements are quite low.
Once your users start meshing and solving larger models, however, they can quickly exceed their local computational resources. Meshing and solving takes both time and RAM. If a model requires more RAM than what is available locally, the computer will become quite unresponsive for some time. Rather than upgrading each computer, you can use Client-Server mode so that users can access a remote computing resource.
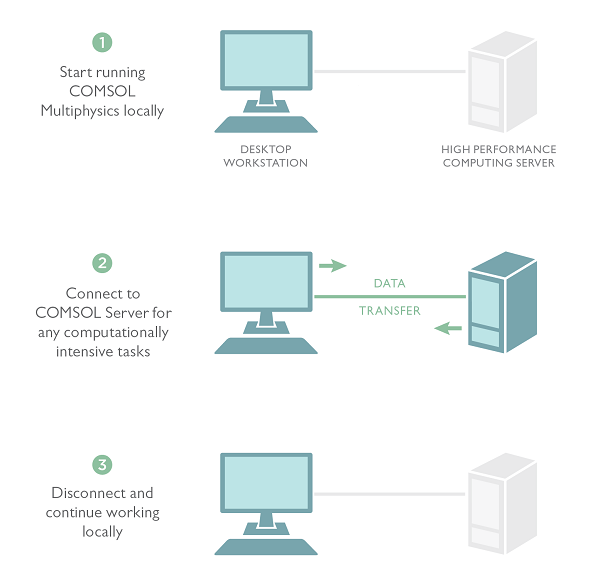
At any time while using COMSOL Multiphysics, it is possible to connect to a remote computing resource via the Client-Server mode of operation. This is a two-step process. First, log onto the remote system and invoke the COMSOL Multiphysics Server, which will start up the COMSOL Multiphysics Server process and open a network connection. Second, on the local machine, simply enter the network connection information into an open session of COMSOL Multiphysics. The software then transparently streams the model data and results back and forth over the network and uses the remote computing resource for all computations.
It is possible to disconnect from the COMSOL Multiphysics Server as long as it is not in the middle of a computation. This will free up the shared computing resource for other users. It can be good practice to do so during postprocessing, which primarily involves visualization of data and is less computationally intensive. Displaying the results is always handled locally, so it is important to have a good graphics card. (Tip: Check out this list of tested graphics cards.)
You can see that running your simulations in Client-Server mode will allow each part of your IT infrastructure do what it does best. You can run the COMSOL Multiphysics Server on your high-performance computing resources, but your users will be working on their local machines for graphics visualization. Other than the number of licenses that you have available, there is no limit to the number of simultaneous users running a server at any one time. In fact, you can run COMSOL Multiphysics in Client-Sever mode all the time. Preprocessing, meshing, solving, and any non-graphical postprocessing computations can all be done on the server. By taking advantage of your organization’s shared computing resources, your users will not need an upgrade of their desktop computer every time they want to run a larger COMSOL Multiphysics model.
Floating Network License Gives You Flexibility
The COMSOL Client-Server capabilities, available as part of the Floating Network License, allow you to run your large COMSOL Multiphysics models on the best computers that you have available, so you do not have to buy every user a large workstation. It is a great option for any organization.
Further Resources
- Please contact us if you would like to learn more
- Learn how to update an FNL



Comments (0)