Blog Posts Tagged Technical Content
Solving Multiphysics Problems
Here we introduce the two classes of algorithms used to solve multiphysics finite element problems in COMSOL Multiphysics. So far, we’ve learned how to mesh and solve linear and nonlinear single-physics finite element problems, but have not yet considered what happens when there are multiple different interdependent physics being solved within the same domain.

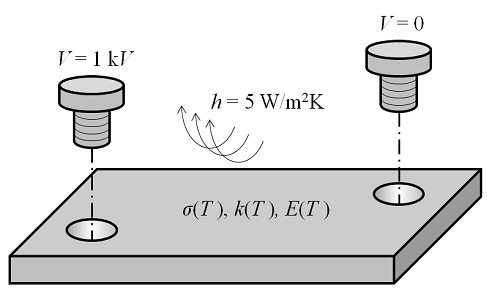
Thermal Modeling of Surfaces with Wavelength-Dependent Emissivity
Whenever we are solving a thermal problem where radiation is significant, we need to know the emissivities of all of our surfaces. Emissivity is a measure of the ability of a surface to emit energy by radiation, and it can depend strongly upon the wavelength of the radiation. This is very relevant for thermal problems where the temperature variation is large or when there is exposure to a high-temperature source of radiation such as the sun. In this post on […]
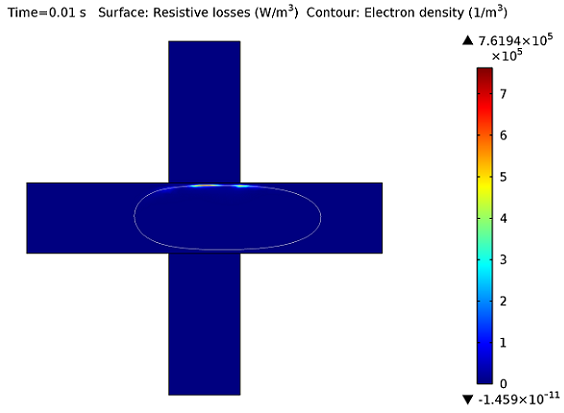
Microwave Plasmas
Microwave plasmas, or wave-heated discharges, find applications in many industrial areas such as semiconductor processing, surface treatment, and the abatement of hazardous gases. This blog post describes the theoretical basis of the Microwave Plasma interface available in the Plasma Module.
Meshing Considerations for Nonlinear Static Finite Element Problems
As part of our solver blog series we have discussed solving nonlinear static finite element problems, load ramping for improving convergence of nonlinear problems, and nonlinearity ramping for improving convergence of nonlinear problems. We have also introduced meshing considerations for linear static problems, as well as how to identify singularities and what to do about them when meshing. Building on these topics, we will now address how to prepare your mesh for efficiently solving nonlinear finite element problems.
COMSOL 4.4 Brings Particle-Field and Fluid-Particle Interactions
The trajectories of particles through fields can often be modeled using a one-way coupling between physics interfaces. In other words, we can first compute the fields, such as an electric field, magnetic field, or fluid velocity field, and then use these fields to exert forces on the particles using the Particle Tracing Module. If the number density of the particles is very large, however, the particles begin to noticeably perturb the fields around them, and a two-way coupling is needed […]
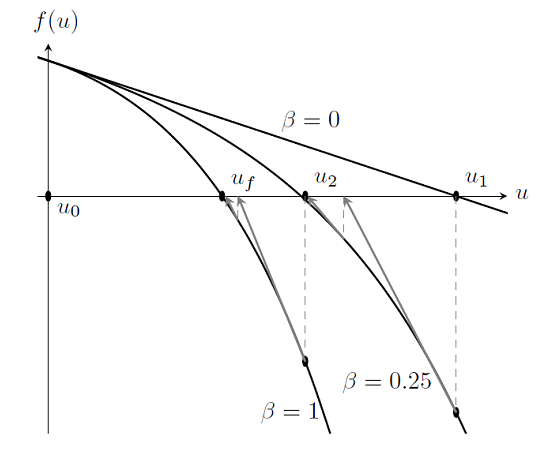
Nonlinearity Ramping for Improving Convergence of Nonlinear Problems
As we saw in “Load Ramping of Nonlinear Problems“, we can use the continuation method to ramp the loads on a problem up from an unloaded case where we know the solution. This algorithm was also useful for understanding what happens near a failure load. However, load ramping will not work in all cases, or may be inefficient. In this posting, we introduce the idea of ramping the nonlinearities in the problem to improve convergence.
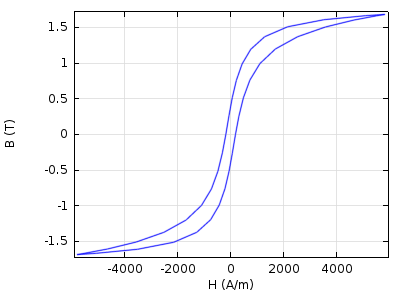
COMSOL 4.4: Magnetic Saturation Curves at your Fingertips
When designing inductive devices, both challenges and possibilities are associated with the nonlinear behavior of ferromagnetic materials. COMSOL Multiphysics is well-adapted to the solution of highly nonlinear numerical models but high-fidelity modeling of nonlinear inductive devices also requires accurate material data. To meet this challenge, a library of 165 nonlinear magnetic materials is provided in COMSOL 4.4, bringing new powers to the design and modeling of electric motors, transformers, relays, etc. Here, we will discuss how the modeling process is […]
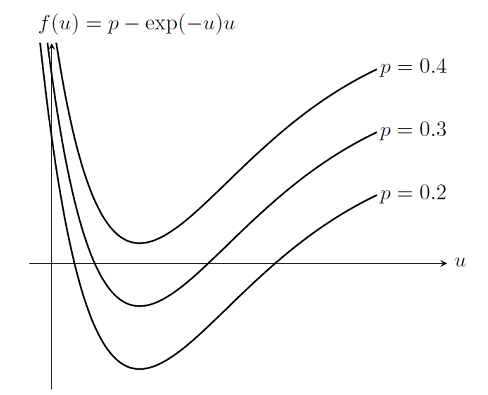
Load Ramping of Nonlinear Problems
As we saw previously in the blog entry on Solving Nonlinear Static Finite Element Problems, not all nonlinear problems will be solvable via the damped Newton-Raphson method. In particular, choosing an improper initial condition or setting up a problem without a solution will simply cause the nonlinear solver to continue iterating without converging. Here we introduce a more robust approach to solving nonlinear problems.
