A COMSOL App to analyse bacteria lethality during sterilization processes
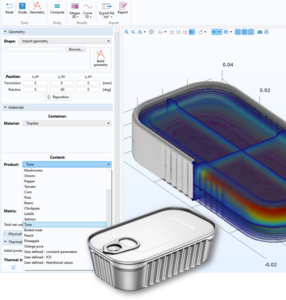
Food sterilization is a thermal industrial process used to give products in airtight food packaging shelf life, stability and safety from a microbiological point of view. The term sterilization mainly includes treatments at high temperatures (greater than 100 °C), even in pressurized devices. This study aims to numerically investigate the effectiveness of the heat penetration process inside the food product during sterilization. It also seeks to evaluate bacterial lethality indexes during the process, based on established formulas available in the reference scientific and technical literature. The COMSOL Model Builder has been used to build a source model solving the transient conductive / convective heat transfer from a temperature-controlled environment to the canned food content. The model is generated in a parametric form to allow the end user, during execution, to input and/or select geometric, constitutive, and functional input data related to the specific product/process for each simulation. A numerical-experimental validation activity confirms the effectiveness of the simulation results. The COMSOL Application Builder and the COMSOL Compiler were then used to build an executable stand-alone interface, which can be used by the end-user to run the simulations of interest. Several features were employed to automate the search and import from the local file system of the reference geometry (file import) and its positioning (input field, data display), the selection from a library of the thermophysical properties of the food content and the container materials (combo box, choice list, methods), the reference thermal cycle, and the handling conditions (static, oscillating, orbiting) of the product (slider, methods), and in general to refine the graphical content of the interface (graphics, forms, ribbon, button, splash). Three-dimensional solid geometries of generic container shapes can be automatically loaded into the simulation environment, along with various types of food products and specific reference thermal treatments. In the absence of reference data for the thermophysical properties of a specific product, these can be automatically calculated by entering the percentages of its basic nutritional contents (carbohydrates, proteins, fats, fibres, ash). The retort temperature profile over time can also be imported from any experimental reference data or defined in a simplified manner by providing the temperature and duration of the heating ramp, the thermal plateau phase, and the final cooling. The main quality indices of the sterilization process, such as the bacterial lethality index (F0), the heat penetration factor (fh), and the lag factor (Jc), are made available to the user through automatic post-processing actions, along with a summary report in an editable format.
Download
- petrone_10951_poster.pdf - 1.52MB
- 1_angelo_barbagallo.pdf - 2.94MB
