New Design and Analysis of Lead Acid Battery Grid
Lead-acid battery is a reversible battery used generally automotive industry. A lead-acid battery cell contains two electrodes with pasted active material, an electrolyte and a separator. Electrode transmits current with electrons whereas electrolyte transmits current with ions. A grid is a solid electrode called as a current collector. It has a lug located usually top of the grid frame. Lug collects and transfers current between two electrodes which are positive and negative electrodes. An electrolyte consists of sulfuric acid that carry ions. A grid is affected by some parameters while conducting current. The parameters can be conductivity of grid material, grid shape, internal resistance, thickness, temperature, and active material mass. In order to obtain uniform current and potential distribution on a grid, a test setup is needed, but it can be expensive, and more time is required. Thus, a grid model can be developed to understand current and potential behavior on grid by saving cost and time before the manufacture.
In this study, Electrochemistry Module was used and analysis with Primary Current Distribution interface for the model of lead acid battery grids, and Lead-Acid Battery interface for the model of 2 V lead acid battery cell. While creating the models, the Application Library was utilized. They are 'Discharge and Self-Discharge of a Lead-Acid Battery' from the application library and 'Primary Current Distribution in a Lead-Acid Battery Grid Electrode' from COMSOL® website. The simulation parameters and equations were selected by the experts and using the results of the experiments in the company.
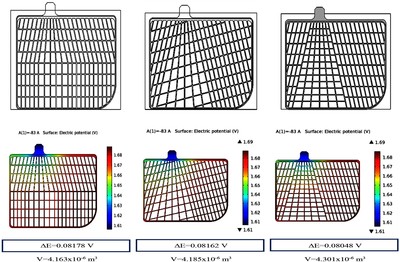
The study aim is to improve the shape of the grid of the most commonly still used lead acid battery to obtain more uniform distribution of the current and the potential and also the current and the potential drop at a minimum to make more efficient lead-acid battery performance with less lead. Therefore, a more efficient grid design can be obtained with less lead. 3D mathematical grid models were designed with COMSOL Multiphysics® to estimate the behavior of the grid under certain conditions to save time and cost. In this model, firstly, the electrodes were made with pasted active material and by adding electrolyte part adjacent to the electrode. The models were worked by considering the thermodynamics behaviors of grid, and then, the optimum grid design and optimum active material mass was found. Later, the 3D mathematical model of the 2 V lead-acid battery was simulated by considering the thermodynamic and kinetic effects of the battery under certain conditions in order to measure the effect of the obtained grid geometries on the performance of the battery. These results can provide us with information before installing the test setup. In this way, we can achieve more efficient results with fewer experiments and also save time and costs. In conclusion, thanks to the new grid designs, a less potential and current drop with less lead, and a more homogeneous potential and current distribution are achieved.
Download
- Cambridge_2019_Tugce_Isler.pptx - 1.89MB
