PIC simulation of a 2.45 GHz ECR ion source using Comsol tensorial permittivity RF capability
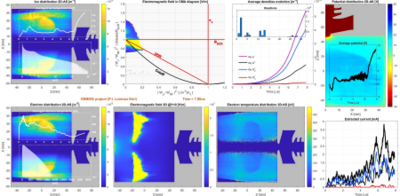
Particle In Cell (PIC) simulation tool for the simulation of 2.45GHz ECR ion source was developed tanks to Comsol Multiphysics RF module capability to compute electromagnetic field propagation imposing a tensorial permittivity with real and complex parts. A tensorial description is necessary because electromagnetic field propagation occurs in non-homogeneous and non-uniform magnetized plasma. The magnetic configuration of the ECR ion source under study and the plasma density evolution intercept different resonances: Electron Cyclotron Resonance, Critical Electron Density, Upper Hybrid Resonance, R-cutoff, and L-cutoff. The result was fascinating because it shows the conversion of electromagnetic waves depending on their position in the CMA diagram and their capability to ignite electrostatic waves. With this software, we intend to disclose why the HSMDIS* magnetic configuration produces higher beam stability than the standard magnetic configuration used in this type of ion source. The PIC simulation tool is developed using Matlab, parallelized functions written in C and “LiveLink for Matlab” module to export the tensorial permittivity map from Matlab to Comsol and import in Matlab the electromagnetic field computed in Comsol. The best mesh and solver configurations are shown with the performance reached with a dual AMD 9654 CPU with 1.6TB of RAM.
Download
- neri_9051_poster.pdf - 1.52MB
- 4_lorenzo_neri.pdf - 3.16MB
